Intentional hydrolysis to overcome the hydrolysis problem: detection of Ce(iv) by producing oxidase-like nanozymes with F−†
Abstract
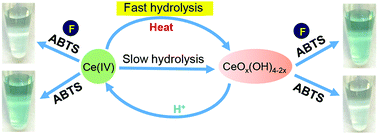
Polyvalent metal ions are susceptible to hydrolysis, making their reproducible detection by sensors and biosensors difficult. We herein turned this disadvantage into an advantage to develop a high selectivity colorimetric method for detecting Ce(IV) by intentionally hydrolyzing it through heating, where subsequent addition of F− recovered the activity, allowing a detection limit of 3.8 μM Ce(IV).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...