A hydroxylamine probe for profiling S-acylated fatty acids on proteins†
Abstract
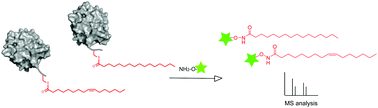
Reversible S-palmitoylation is a key regulatory mechanism of protein function and localization. There is increasing evidence that S-acylation is not restricted to palmitate but it includes shorter, longer, and unsaturated fatty acids. However, the diversity of this protein modification has not been fully explored. Herein, we report a chemical probe that combined with MS-based analysis allows the rapid detection and quantification of fatty acids linked to proteins. We have used this approach to profile the S-acylome and to show that the oncogene N-Ras is heterogeneously acylated with palmitate and palmitoleate. Studies on protein distribution in membrane subdomains with semisynthetic proteins revealed that unsaturated N-Ras presents an increased tendency toward clustering and higher insertion kinetic rate constants.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...