Achieving 59% faradaic efficiency of the N2 electroreduction reaction in an aqueous Zn–N2 battery by facilely regulating the surface mass transport on metallic copper†
Abstract
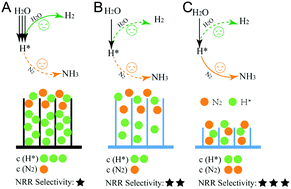
Herein, for the first time, we find that the surface mass transport properties of catalysts play critical roles in determining the electrocatalytic NRR selectivity over the competitive HER in aqueous media on metallic Cu. In particular, by controlling the monolayer thickness of Cu nanoparticles with a minimum mass transport barrier, the faradaic efficiency (FE) of the NRR can be dramatically enhanced to 33% in the H-type cell test and even to 59% in a new-type Zn–N2 aqueous battery.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...