Surface oxygen vacancy defect engineering of p-CuAlO2via Ar&H2 plasma treatment for enhancing VOCs sensing performances†
Abstract
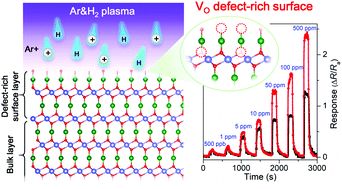
Ar&H2 plasma treatment was proposed to enhance the response of a p-CuAlO2 sensor toward volatile organic compounds. Comprehensive defect characterization studies indicate a substantial increase of surface unsaturated oxygen vacancy (VO) defects via plasma treatment, which could provide active sites for molecule adsorption and the subsequent interfacial redox reaction.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...