Design and synthesis of capped-paddlewheel-based porous coordination cages†
Abstract
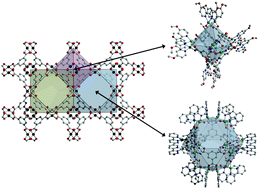
To leverage the structural diversity of metal–organic frameworks, the ability to controllably terminate them for the isolation of porous coordination cages is advantageous. However, the strategy has largely been limited to ligand termination methods, particularly for paddlewheel-based materials. Here, we show a paddlewheel-capping strategy can be employed to afford previously unattainable coordination cage structures that are mimetic of metal–organic framework pores.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...