Morphology-dependent electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction on Ag triangular nanoplates†
Abstract
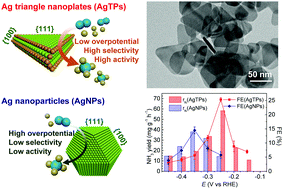
Electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction reactions (ENRR) can produce ammonia from nitrogen and water under ambient conditions. Here, we report the morphology-dependent electro-catalytic nitrogen reduction on Ag triangular nanoplates. Boosted by potassium cations, Ag triangular nanoplates with sharp edges exhibit a high faradaic efficiency of 25% with an ammonia yield of 58.5 mg gAg−1 h−1 at a low overpotential of −0.25 V vs. RHE. In comparison, rounded Ag nanoparticles mainly enclosed by {111} and {100} surfaces show a much smaller faradaic efficiency of 16% and ammonia yield of 38 mg gAg−1 h−1 at a larger overpotential (−0.35 V vs. RHE).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...