Efficient synthesis and enzymatic extension of an N-GlcNAz asparagine building block†
Abstract
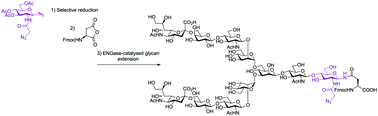
N-Azidoacetyl-D-glucosamine (GlcNAz) is a particularly useful tool in chemical biology as the azide is a metabolically stable yet accessible handle within biological systems. Herein, we report a practical synthesis of FmocAsn(N-Ac3GlcNAz)OH, a building block for solid phase peptide synthesis (SPPS). Protecting group manipulations are minimised by taking advantage of the inherent chemoselectivity of phosphine-mediated azide reduction, and the resulting glycosyl amine is employed directly in the opening of Fmoc protected aspartic anhydride. We show potential application of the building block by establishing it as a substrate for enzymatic glycan extension using sugar oxazolines of varying size and biological significance with several endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidases (ENGases). The added steric bulk resulting from incorporation of the azide is shown to have no or a minor impact on the yield of enzymatic glycan extension.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...