Tunable regulatory activities of 1,10-phenanthroline derivatives towards acid sphingomyelinase and Zn(ii)–amyloid-β†
Abstract
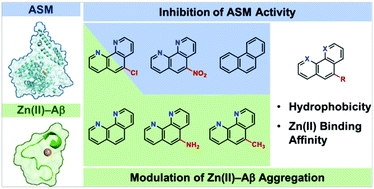
We report a new series of small molecules able to achieve the tunability of modulatory activities against acid sphingomyelinase (ASM) and Zn(II)-bound amyloid-β [Zn(II)–Aβ], two pathological targets found in the brain affected by Alzheimer's disease. Rational tuning of the hydrophobicity and Zn(II) binding affinity of the 1,10-phenanthroline (phen) framework successfully yielded compounds as chemical modulators for ASM (4 and 5), Zn(II)–Aβ (phen, 1, and 2), or both (3).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...