Tetraphenylethene-based tetracationic cyclophanes and their selective recognition for amino acids and adenosine derivatives in water†
Abstract
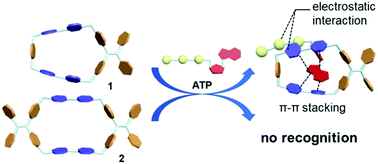
Two new tetracationic cyclophanes 1 and 2 containing tetraphenylethene and bipyridinium moieties were synthesized via a two-step SN2 reaction. These water-soluble cyclophanes with a cationic and hydrophobic cavity exhibited selective recognition for amino acids (e.g. tryptophan) and adenosine derivatives (e.g. ATP) via electrostatic and π–π interactions in water.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...