Engineering graphene oxide with ultrasmall SPIONs and smart drug release for cancer theranostics†
Abstract
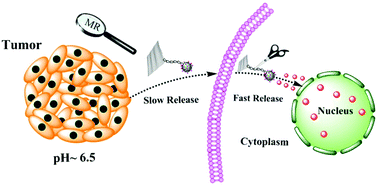
A smart nanotheranostics nanoplatform was constructed using engineered graphene oxide and the in situ growth of ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide particles (SPIONs). The construction of such a novel theranostics nanoplatform shows great potential in tumor theranostics, especially for T1-weighted magnetic resonance (T1-MR) imaging guided, pH-sensitive chemotherapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...