H2O2-activated oxidative stress amplifier capable of GSH scavenging for enhancing tumor photodynamic therapy†
Abstract
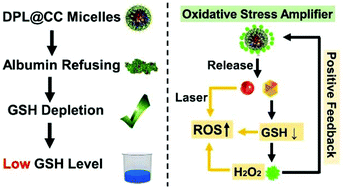
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a clinically approved cancer treatment approach that relies on the generation of excess reactive oxygen species (ROS) to eradicate tumor cells by inducing oxidative stress. Unfortunately, if the tumor's endogenous glutathione (GSH) is overexpressed, it will eliminate the ROS and restrict the therapeutic efficacy of PDT. Herein, we report a H2O2-activated oxidative stress amplifier (OSA) for enhancing the ROS generation for PDT via GSH scavenging. Cinnamaldehyde (Cin) and chlorin e6 (Ce6) were applied as the GSH scavenger and photosensitizer, respectively, which were assembled with the ROS-responsive amphipathic polymer (DPL) to form DPL@CC micelles as the OSA. In the circulation of blood, the OSA can effectively protect the Cin from albumin binding to retain its GSH depletion ability. Once the OSA reached the tumor site, the high level of H2O2 triggered the degradation of DPL and led to the release of Cin and Ce6. Subsequently, the released Cin reacted with the intracellular GSH by Michael Addition and downregulated the GSH level to about 18.9%, versus untreated cells, to weaken the anti-oxidation ability of tumor cells. Thus, it provided a suitable environment for PDT to obtain an amplifying effect on oxidative stress and superior anti-cancer efficacy of 94% growth inhibition. The preparation of the H2O2-activated oxidative stress amplifier is a convincing strategy for promoting intracellular ROS generation and enhancing the tumor PDT efficacy, which could also augment the clinical application of PDT.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...