Heparan sulfate proteoglycan promotes fibroblast growth factor-2 function for ischemic heart repair
Abstract
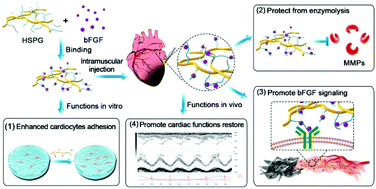
It is well known that the basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) promotes angiogenesis after myocardial infarction (MI), but its biological functions decrease in the event of diffusion, enzymolysis, and weak binding with co-receptors in vivo. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPG) are a major component of extracellular matrices and have been shown to regulate a wide range of cellular functions and bioprocesses by acting as a co-receptor for bFGF and affecting its bioactivities. However, the influence of HSPG on the function of bFGF after myocardial infarction is unknown. Here, exogenous HSPG along with bFGF was injected into the hearts of rats to deliver the angiogenic growth factor for ischemic heart repair following induced MI. The specific binding of HSPG with bFGF protein was demonstrated, which was about 6-fold stronger than the binding of bFGF with heparin. The biological mechanisms of HSPG binding with bFGF were further studied by cell adhesion assay, and assays of bFGF and matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP2) activities demonstrated that HSPG enhances cell adhesion, promotes the bioactivity of bFGF in angiogenesis, and protects bFGF from enzymolysis. Our results indicate that HSPG has potential clinical utility as a delivery agent for heparin-binding growth factors. Additionally, HSPG shows high binding affinities with different ECM proteins which also help to anchor bFGF to heart tissue. Therefore, extracellular proteins that mimic the bio-scaffold of the extracellular matrix could promote the activities of bFGF to facilitate ischemic heart repair.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...