Systematic acute and subchronic toxicity evaluation of polysaccharide–protein complex-functionalized selenium nanoparticles with anticancer potency†
Abstract
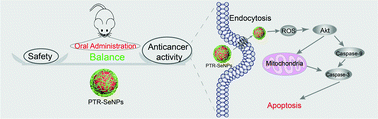
Functionalized selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) have demonstrated potential for applications in cancer chemotherapy, radio-sensitization, nephroprotection and drug delivery. However, their clinical application requires further systemic safety evaluation. Therefore, in this study, we examine the systematic acute and subchronic toxicity of polysaccharide–protein complex coated SeNPs (PTR-SeNPs). These particles exhibited a low oral acute toxicity (higher LD50) in SPF grade ICR mice and SD rats, and the evaluation of subchronic toxicity demonstrated that the no observed effect level (NOAEL) of the PTR-SeNPs was less than 200 μg Se per kg BW per day, which is about 30 times the tolerable upper intake levels of Se in the human body. In addition, we also found that, under a safe dose (0.75–7.5 mg kg−1), the oral administration of PTR-SeNPs dramatically inhibited the growth of cancer in a tumor-bearing nude mouse model, and the results of the histological analysis indicated that PTR-SeNPs did not significantly damage the major organs, including the liver, spleen, heart, kidneys and lungs. Moreover, the induction of caspase activation and mitochondrial dysfunction was the major anticancer action mechanism of PTR-SeNPs. Taken together, the results of this study provide a simple approach for the facile and large-scale manufacturing of SeNPs with reduced toxicity and enhanced anticancer activity through the regulation of the surface properties of SeNPs. Furthermore, this study generates evidence for the future exploration and translational application of these materials through oral administration in nanomedicine and nutritional sciences.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...