Engineering natural matrices with black phosphorus nanosheets to generate multi-functional therapeutic nanocomposite hydrogels†
Abstract
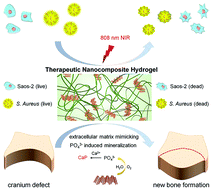
Natural polysaccharides and proteins have been widely explored for the preparation of hydrogel matrices due to their promising biocompatibility and biodegradability. However, it is challenging to achieve multiple functions of the hydrophilic matrix through convenient functionalization strategies. Herein we report the facile engineering of a natural matrix with black phosphorus (BP) nanosheets as building blocks to generate a therapeutic nanocomposite hydrogel (BP/Gel) with an array of promising features. BP nanosheets could reinforce the crosslinking networks and significantly promote their capabilities of mineralization. The BP/Gel nanocomposite hydrogel exhibits excellent near infrared (NIR) photothermal performance and good biocompatibility in vitro and in vivo. Upon NIR irradiation, the nanocomposite hydrogel demonstrates efficient photothermal antibacterial features. More remarkably, the BP nanosheet engineered hydrogel matrix is capable of promoting in vitro osteogenesis in the absence of osteoinductive factors, and in the meantime demonstrates significant newborn cranial bone tissue formation in a Sprague-Dawley rat model. These results demonstrate that BP nanosheets could endow the natural matrix with multiple functions including reinforced networks, photothermal performance, enhanced mineralization and bone regeneration, which provides a facile and highly efficient therapeutic strategy for bone tissue engineering.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...