Esterase-sensitive cleavable histone deacetylase inhibitor-coupled hyaluronic acid nanoparticles for boosting anticancer activities against lung adenocarcinoma†
Abstract
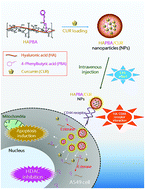
4-Phenylbutyric acid (PBA)-installed hyaluronic acid (HA)-based nanoparticles (NPs) were developed for amplifying the anticancer potential of curcumin (CUR) for lung cancer therapy. PBA was introduced to the HA backbone as a hydrophobic segment of a nanoassembled structure and as a histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor for cancer therapy. PBA was released from the HA–PBA conjugate (HAPBA) via an esterase-responsive cleavage of ester bonds in cancer cells and may affect the dissociation of NP structure. CUR-entrapped HAPBA-based NPs, with 265 nm hydrodynamic size, unimodal size distribution, negative zeta potential, and sustained drug release, were fabricated. Co-treatment of A549 cells by PBA and CUR elevated the antiproliferation efficiency compared with CUR-treatment. CUR-loaded HAPBA NPs also exhibited a significantly lower IC50 value compared with the CUR and HAPBA10 + CUR groups (p < 0.05). Cy5.5-labeled HAPBA NPs containing CUR group displayed higher accumulation in tumor tissue and less distribution in liver and spleen after intravenous injection compared with the Cy5.5-injected group in A549 tumor-bearing mouse model. Multiple dosing of CUR-loaded HAPBA NPs in A549 tumor-bearing mouse model exhibited efficient tumor growth suppression and apoptosis-inducing effects. CD44 receptor targeting and HDAC inhibiting HAPBA NPs can be used to boost the anticancer potentials of drug cargo for the therapy of CD44 receptor-expressed cancers.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...