Immobilized Candida antarctica lipase B catalyzed synthesis of biodegradable polymers for biomedical applications
Abstract
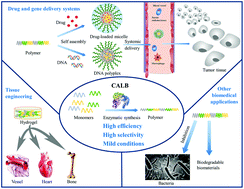
Enzymes, as green catalysts, can catalyze varied reactions with high efficiency. Among various types of enzymes, Candida antarctica lipase B (CALB) is the most commonly used one, due to its high catalytic activity in polymer synthesis. This review highlights the polymers synthesized via the catalysis of immobilized CALB, and focuses on their applications in biomedical areas, especially their use in drug and gene delivery systems. Upholding the idea of sustainable and environment-friendly green chemistry, and emphasizing the safety of products applied for biomedical uses, lipase catalysts are better choices compared to inorganic metal catalysts. We introduced the background and advantages of lipase catalysis and reviewed the lipase-catalyzed synthetic routes involving ring opening polymerization, polycondensation and others. For biomedical applications, we mainly discuss enzymatically synthesized polyesters, due to their outstanding biodegradability and synthetic possibilities. We firstly introduced our early work as basic thinking, then we summarized the subsequent work that focused on developing multiple functional polyesters for different biomedical applications. Prominent experimental results have been shown and the significance of CALB-catalyzed synthesis has been proved.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...