Enhancement of siRNA transfection by the optimization of fatty acid length and histidine content in the CPP†
Abstract
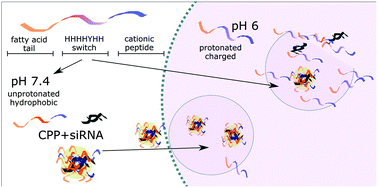
Extracellular synthetic nucleic acids, such as siRNAs, are unable to reach their intended targets efficiently. Therefore, delivery methods such as cell-penetrating peptides (CPP), which increase their transport, could enhance the potency of siRNA as therapeutic agents. The CPP NickFect55 (NF55) is an efficient peptide-based delivery vector, which has been previously used to deliver plasmid DNA into cells in vivo. To achieve higher intracellular delivery and bioactivity from the delivered cargo, we designed a series of histidine-containing peptides by optimizing pH-sensitivity, net charge, hydrophobicity, and charge distribution in the sequence of the CPP NF55. In the current work, we have applied a strategy where we have replaced amino acids in the C-terminus of the peptide in order to distribute hydrophobic and hydrophilic amino acids into distinct regions along the alpha-helical projection, including histidine amino acids into the sequence at the N-terminus, and optimizing the N-terminal fatty acid modification to suit the specific peptide sequence. We tested the CPPs based on the transfection efficacy, CPP/siRNA complex stability, and the properties of the CPPs, such as hemolytic activity, buffering capability and cell toxicity. As a result, we have introduced a new peptide with a completely redesigned N-terminus that displays adaptive response to its physical environment. This peptide – NickFect70 (NF70) – efficiently condenses siRNA, protects the cargo against degradation and effectively mediates target gene knockdown both in mammalian cell culture and in vivo, in a mouse model.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...