Screening a specific Zn(ii)-binding peptide for improving the cognitive decline of Alzheimer's disease in APP/PS1 transgenic mice by inhibiting Zn2+-mediated amyloid protein aggregation and neurotoxicity†
Abstract
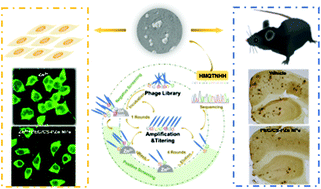
Zn2+ has been implicated in the progression of Alzheimer's disease (AD), as amyloid-β protein (Aβ) aggregation and neurotoxicity are mediated by zinc ions. Therefore, development of metal chelators for inhibiting and regulating metal-triggered Aβ aggregation has received attention as a strategy for treating AD. Here, we used an approach based on phage display to screen for a Zn(II)-binding peptide that specifically blocks Zn-triggered Aβ aggregation. A fixed Zn(II) resin was prepared using Ni-IDA affinity resin, and the target Zn(II) was screened by interaction with a heptapeptide phage library. After negative biopanning against IDA and four rounds of positive biopanning against Zn(II), high specificity Zn(II)-binding phages were obtained. Through DNA sequencing and ELISA, 15 sets of Zn(II)-binding peptides with high histidine contents were identified. We chose a highly specific peptide against Zn(II) with the sequence of H-M-Q-T-N-H-H, and its abilities to chelate Zn2+ and inhibit Zn2+-mediated Aβ aggregation were assessed in vitro. We loaded the Zn(II)-binding peptide onto PEG-modified chitosan nanoparticles (NPs) to improve the stability and the bioavailability of the Zn(II) binding peptide. PEG-modified chitosan NPs loaded with Zn(II)-binding peptide (PEG/PZn-CS NPs) reduced Zn2+ concentrations and Aβ secretion in mouse neuroblastoma (N)2a cells stably over-expressing the APP Swedish mutation (N2aswe). Zn2+-Induced neurotoxicity, oxidative stress, and apoptosis were attenuated by PEG/PZn-CS NPs. Intranasal administration of PEG/PZn-CS NPs improved the cognitive ability of APPswe/PS1d9 (APP/PS1) double-transgenic mice and reduced Aβ plaques in the mouse brain. This study indicated that a Zn(II)-binding peptide and its NPs have promise as a potential anti-AD agent.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...