Indocyanine green binds to DOTAP liposomes for enhanced optical properties and tumor photoablation†
Abstract
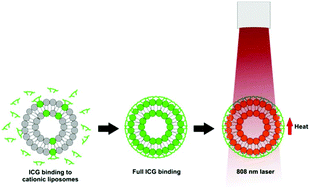
Indocyanine green (ICG) is a clinically-approved near infrared (NIR) dye used for optical imaging. The dye is only slightly soluble in water and is prone to aggregation in saline solutions, so that alternative formulations can improve photophysical performance. Numerous nanoscale formulations of ICG have been described in the literature, but we sought to develop an approach that does not require additional purification steps. Pre-formed liposomes incorporating 45 mol% of the cationic lipid 1,2-dioleoyl-3-trimethylammonium-propane (DOTAP) rapidly bind ICG, resulting in enhanced NIR optical properties. ICG binding is dependent on the amount of DOTAP incorporated in the liposomes. A dye-to-lipid mass ratio of [0.5 : 25] is sufficient for full complexation, without additional purification steps following mixing. NIR absorption, fluorescence intensity, and photoacoustic signals are increased for the liposome-bound dye. Not only is the optical character enhanced by simple mixing of ICG with liposomes, but retention in 4T1 mammary tumors is observed following intratumor injection, as assessed by fluorescence and photoacoustic imaging. Subsequent photothermal therapy with 808 nm laser irradiation is effective and results in tumor ablation without regrowth for at least 30 days. Thus, ICG optical properties and photothermal ablation outcomes can be improved by mixing the dye with pre-formed DOTAP liposomes in conditions that result in full dye-binding to the liposomes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...