In situ synthesis, stabilization and activity of protein-modified gold nanoparticles for biological applications
Abstract
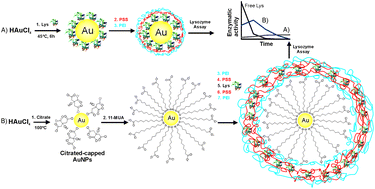
Herein, we demonstrate the use of lysozyme (Lys) as a model to fabricate a protein carrier system based on gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) via the Layer-by-Layer (LbL) technology. Poly(ethyleneimine) (PEI) and poly(sodium 4-styrenesulfonate) (PSS) were used as cationic and anionic polymers respectively to grow oppositely charged layers. Mild aqueous conditions were utilized to avoid protein denaturation and activity instead of organic solvents that have been used in other encapsulation systems. Two different strategies were used: (A) lysozyme acting as a reducing and stabilizing agent in the formation of AuNPs at a temperature of 45 ± 2 °C followed by only two subsequent polymeric layers deposited by LbL, and (B) citrate acting as a reducing agent prior to stabilization of the AuNPs by mercaptoundecanoic acid. Dynamic light scattering, UV-vis spectroscopy, IR spectroscopy and transmission electron microscopy were used to characterize the nanoconjugates. Furthermore, the enzymatic activity of the resulting protein/nanoparticle conjugates was evaluated using the bacteria Micrococcus lysodeikticus as a substrate.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...