POSS-based supramolecular amphiphilic zwitterionic complexes for drug delivery†
Abstract
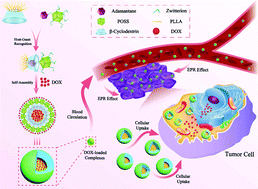
Zwitterionic complexes in aqueous solutions have been extensively explored as the most promising candidate in drug delivery systems for targeted cancer chemotherapy. A POSS-based supramolecular AD-POSS-(sulfobetaine)7/CD-PLLA zwitterionic complex has been fabricated via a combination of efficient click chemistry and host–guest interaction. The well-defined POSS-based zwitterionic polymer could self-assemble into spherical nanoparticles that encapsulated a model cancer drug (DOX) and exhibited drug release in a controlled manner in a faintly acidic environment. On account of the hydrophilic block with cationic and anionic groups in the microscopic range that can form a hydration layer via electrostatic interactions, these drug-loaded nanoparticles exhibited excellent stability in a tumor intracellular microenvironment or under other pH conditions as revealed by dynamic light scattering (DLS) and zeta potential measurements. In vitro experiments demonstrated that these POSS-based nanoparticles had high resistance to non-specific protein absorption and low cytotoxicity against normal cells. Moreover, these DOX-loaded aggregates could be accumulated and effectively internalized by HeLa and MCF-7 tumor cells, exhibiting effective cellular proliferation inhibition via the release of anticancer agents. Therefore, these POSS-based supramolecular amphiphilic zwitterionic complexes, relying on the simple supramolecular interaction and efficient click reaction, could further emerge as a potential universal anticancer drug nanocarrier system for multifunctional cancer chemotherapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...