Tyrosine based cationic acrylates as potent antimicrobial agents against shigellosis†
Abstract
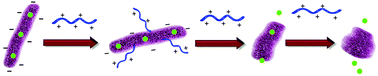
Incorporation of tyrosine within synthetic macromolecules via the controlled radical polymerization technique is of particular interest due to the presence of a phenolic group in tyrosine imparting high inhibition potential. Tyrosine incorporation is also fascinating from a medicinal point of view since this particular amino acid is present in several natural antimicrobial peptides as a key constituent. This study describes a facile strategy to integrate the naturally occurring proteinogenic amino acid tyrosine within a polyacrylate system via the reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer polymerization technique to construct potent bioactive macromolecules against the microbial strain S. flexneri 2a causing shigellosis. The cationic charge and amphiphilic features inherited from the amino acid tyrosine mimic the function of natural antimicrobial peptides. A library of tyrosine polyacrylates has been synthesized to investigate the effect of molecular weight on antimicrobial activity. The time-dependent morphological switching observed via FESEM measurement revealed membrane rupture followed by leakage of cellular constituents as an effective mechanism of action of the biomimetic tyrosine-based polymers. The details of membrane disintegration and depolarization due to alteration in membrane potential have been evaluated via flow cytometric and fluorescence microscopic measurements. Most importantly, the side chain tyrosine-based polymers show fascinating biocidal features against the Gram-positive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) bacterial strain, the major causative agent of nosocomial infections. The broad spectrum nature of the polymers has been further investigated against the fungus Aspergillus niger and another Gram-negative bacterium, Escherichia coli.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...