A Nd3+ sensitized upconversion nanosystem with dual photosensitizers for improving photodynamic therapy efficacy†
Abstract
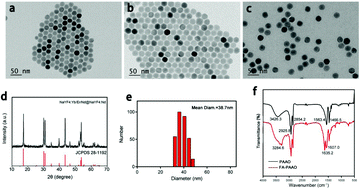
The efficacy of photodynamic therapy (PDT) was greatly hindered by the use of a 980 nm laser with undesired overheating effects as well as low reactive oxygen species (ROS) yields. Herein, we address these problems using a dual-photosensitizer (PS) loaded upconversion nanoparticle (UCNP) system. In detail, the NaYF4:Yb/Er/Nd@NaYF4:Nd core–shell UCNP system was designed to exhibit 808 nm laser excitation ability to avoid unfavorable thermal effects. More importantly, the co-encapsulation of dual PS, in terms of merocyanine 540 (MC540) and zinc phthalocyanine (ZnPc), could be respectively triggered by the dual emissions of UCNPs, which could generate sufficient ROS with improved efficiency. Furthermore, in vitro and in vivo studies were conducted to confirm the folate receptor (FR)-overexpressed cancer cell- or tumor-specific targeting ability with minimal side effects on normal tissue, by using this dual PS loaded UCNP system with the modification of the targeting group folic acid (FA). It is worth mentioning that the singlet oxygen production assay and PDT treatment demonstrated significantly enhanced PDT efficacy of the dual-PS approach, in comparison with the single PS method. In short, the FR-targeted dual-PS nanoconstructs maximized the anti-tumor efficacy of PDT by taking advantage of dual fluorescence emission and 808 nm excitation of UCNPs, which might inspire the future development of noninvasive deep-seated tumor treatment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...