Assessment of zero-valent iron-based nanotherapeutics for ferroptosis induction and resensitization strategy in cancer cells†
Abstract
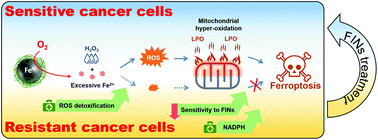
Addressing nanomedicine resistance is critical for its ultimate clinical success; despite this, advancing the therapeutic designs for cancer therapy are rarely discussed in the literature. In this study, we discovered that ferroptosis is the central mechanism governing the therapeutic efficacy and resistance of treatment with zero-valent iron nanoparticles (ZVI NPs). In ZVI-sensitive oral cancer cells, ZVI NPs-induced ferroptosis was characterized by mitochondrial lipid peroxidation and reduced levels of glutathione peroxidases (GPx) in subcellular organelles. However, resistant cells could attenuate ZVI-induced oxidative stress and GPx reduction. They also showed stronger mitochondrial respiration ability, thus resisting ZVI NPs-induced mitochondrial membrane potential loss. Transcriptome comparison and quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) analysis revealed that ZVI-resistant cancer cells expressed a gene set related to enhanced NADPH supply, higher detoxification capacity of reactive oxygen species, and decreased sensitivity to ferroptosis inducers (FINs). Finally, we discovered that certain FINs were able to sensitize ZVI-resistant cancer cells to become treatable without compromising healthy non-malignant cells. These findings suggest that ferroptosis can serve as a druggable target for anti-cancer nanomedicine and therapeutic resistance modulation using ZVI NPs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...