Polymer microchamber arrays for geometry-controlled drug release: a functional study in human cells of neuronal phenotype
Abstract
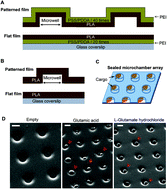
Polyelectrolyte multilayer (PEM) microchambers can provide a versatile cargo delivery system enabling rapid, site-specific drug release on demand. However, experimental evidence for their potential benefits in live human cells is scarce. Equally, practical applications often require substance delivery that is geometrically constrained and highly localized. Here, we establish human-cell biocompatibility and on-demand cargo release properties of the PEM or polylactic acid (PLA)-based microchamber arrays fabricated on a patterned film base. We grow human N2A cells (a neuroblastoma cell line widely used for studies of neurotoxicity) on the surface of the patterned microchamber arrays loaded with either a fluorescent indicator or the ubiquitous excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate. The differentiating human N2A cells show no detrimental effects on viability when growing on either PEM@PLA or PLA-based arrays for up to ten days in vitro. Firstly, we use two-photon (2P) excitation with femtosecond laser pulses to open individual microchambers in a controlled way while monitoring release and diffusion of the fluorescent cargo (rhodamine or FITC fluorescent dye). Secondly, we document the increases in intracellular Ca2+ in local N2A cells in response to the laser-triggered glutamate release from individual microchambers. The functional cell response is site-specific and reproducible on demand and could be replicated by applying glutamate to the cells using a pressurised micropipette. Time-resolved fluorescence imaging confirms the physiological range of the glutamate-evoked intracellular Ca2+ dynamics in the differentiating N2A cells. Our data indicate that the nano-engineering design of the fabricated PEM or PLA-based patterned microchamber arrays could provide a biologically safe and efficient tool for targeted, geometrically constrained drug delivery.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...