Coaxial bioprinting of cell-laden vascular constructs using a gelatin–tyramine bioink†
Abstract
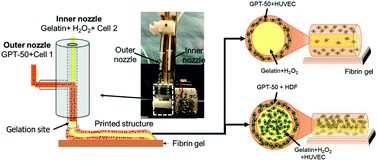
Herein, three-dimensional (3D) bioprinting of engineered constructs with cell-laden biomaterials was investigated for the development of 3D tissue constructs in vitro. The present article proposes a simple coaxial-nozzle-based printing method using a one-step gelling gelatin bioink containing different cell types for vascular structure generation. First, a gelatin bioink prepolymer with a tyramine functional group was synthesized. To facilitate rapid gelation, polyethylene glycol (PEG) was introduced as a spacer between gelatin and tyramine. The gelatin–PEG–tyramine (GPT) prepolymer underwent enzymatic crosslinking, which yielded a higher gelation rate of up to 4.24 ± 0.08 s. Second, one-step bioprinting of a cell-laden tubular structure was demonstrated using a coaxial type extruder and the GPT bioink with human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) with or without human dermal fibroblasts (HDFs). The printed no-cell GPT tube was demonstrated to possess a perfusable vascular structure. The extruded tube with HUVECs-in-GPT sheath configuration resulted in an endothelial cell-lined hollow structure and was maintained for up to 8 days in vitro. Additionally, the coaxially extruded tube with HUVECs-in-core (gelatin) and HDFs-in-GPT sheath (GPT) configuration exhibited a distribution of these two cell types along the tube axis. In the current study, it was demonstrated that a radial distribution of multiple vascular cells can be simply achieved using a synthetic GPT bioink combined with a coaxial nozzle printing system, serving as a proof-of-concept for one-step generation of vascular constructs. The rapid gelling bioink prepolymer, in combination with a coaxial bioprinter nozzle mechanism, has great potential for the development of designed, printed, and organized 3D tissue architecture vascularization.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...