Development of disk-shaped monolithic microplates for detecting multiple mycotoxins†
Abstract
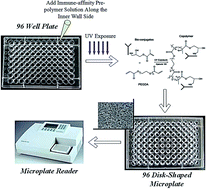
Organic polymer monoliths have been used extensively for separation and purification of molecules because of their excellent mass transfer properties and versatile surface modification. However, organic polymer monolithic materials have significant UV absorption, which blocked UV-visible absorbance detection. Thus, we developed novel disk-shaped mycotoxin immune-affinity monolithic microplates for quantitative detection of mycotoxins. The concentric disk-shaped format allows the obscure organic monoliths to capture mycotoxins and unobstructed UV-visible absorbance measurement was performed in the same microplates. The limits of detection of 96 disk-shaped mycotoxin immune-affinity monolithic microplates were 161.73, 22.52, 0.14, and 0.21 μg kg−1 for Deoxynivalenol (DON), Zearalenone (ZEN), Aflatoxin B1 (AFB1), and Ochratoxin A (OTA), respectively, which meet well the requirements for detection of foodstuffs. The recovery rate ranges of the four mycotoxins were 87–92%, 82–89%, 78–116%, and 83–87% for DON, ZEN, AFB1, and OTA disk-shaped microplates, respectively, which proved that the disk-shaped monolithic microplates have good reproducibility for mycotoxin detection. In summary, 96 disk-shaped mycotoxin immune-affinity monolithic microplates are a sensitive, accurate, stable, and convenient platform for detection of mycotoxins in agro-food.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...