A high throughput screening method for endocrine disrupting chemicals in tap water and milk samples based on estrogen receptor α and gold nanoparticles
Abstract
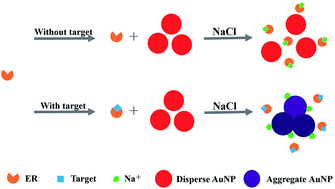
Increasing concern over endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) in environmental and food samples has created the demand for rapid and high throughput screening methods to evaluate their estrogenic effects. In this study, a sensitive assay based on estrogen receptor α (ERα) and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) was established to screen EDCs and confirm the binding affinities of EDCs with ERα. ERα protein can prevent the salt-induced aggregation of AuNPs by recruiting Na+ from AuNPs. When there are EDCs as targets in the sample, the specific binding of ERα and EDCs via hydrogen bonding results in a reduction in the binding between Na+ and ERα, and then most Na+ ions bind to the AuNPs and induce their aggregation. Nine kinds of estrogen-agonist compound, 17β-estradiol (17β-E2), diethylstilbestrol (DES), hexoestrolum (HES), 17α-estradiol (17α-E2), estrone (E1), 2,2-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1,1,1-trichloroethane (HPTE), genistein, bisphenol A (BPA) and bisphenol B (BPB), were chosen as representative targets for the validation of this method. The ranking order of estrogenic potency determined by this method was DES > 17β-E2 > HES > 17α-E2 > E1 > HPTE > genistein > BPA > BPB, which was consistent with the published results. Moreover, the recoveries of the nine kinds of EDCs spiked in tap water and milk samples were all between 80.0% and 120.0%, which proved that this method can be used for the high throughput screening of these EDCs in environmental and food samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...