Optimization of sensors based on encapsulated algae for pesticide detection in water†
Abstract
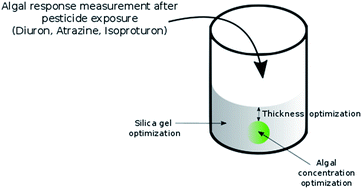
Pesticides represent a significant source of contamination for urban and suburban surface, ground and seawaters. Whole-cell algal biosensors are sensitive, cheap and adaptable early-warning systems, which are capable of detecting pesticides both in situ and continuously in discharges and receiving ecosystems. Here we designed and optimized a new biosensor with a microalgae immobilization method based on double encapsulation in alginate beads/silica gel, which has been proven safe for algae in previous studies. Pesticide detection was assessed by chlorophyll fluorescence disturbance using the two algae strains Chlorella vulgaris and Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. Three pesticides (diuron, atrazine and isoproturon) were used to optimize and assess the sensor's performance. The first step was to select the optimal silica hydrogel (based on porosity and optical properties) to design the sensor. Two parameters were adjusted to obtain the best contact between microalgae and pesticides, optimizing pesticide detection: algal concentrations in the alginate beads and thickness of the silica gel around the algal beads. Finally, the biosensor's performance was assessed with pesticide solutions and the lowest detection limit was obtained with C. vulgaris exposed to diuron (10 μg L−1).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...