Application of carbon dots synthesized from tryptone and yeast extract in bioimaging and highly selective detection of p-nitrophenol and nickel(ii)†
Abstract
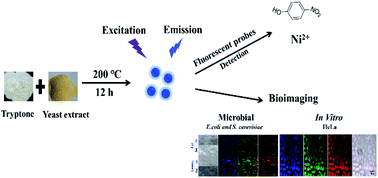
Carbon dots (CDs) possess properties appropriate for application in various fields, especially in environmental pollution detection and biological imaging. With the unprecedented worsening of environmental quality, rapid identification and real-time monitoring of toxic compounds are very important. We successfully synthesized fluorescent CDs doped with tryptone and yeast extract via a hydrothermal process. The readily procured CDs-TY possess good photostability and can be applied as a probe for highly selective, rapid, and facile detection of both p-nitrophenol (p-NP) and Ni2+. The prepared CDs-TY display an excellent linear response to the concentrations of p-NP and Ni2+ in the range of 0.03–20 μM and 0.1–32 μM, respectively. The limit of detection (LOD) for p-NP was as low as 12 nM, which is lower than most reported values thus far. Additionally, HeLa cells and microbial cells were employed to explore the application of CDs-TY in bioimaging in vitro. CDs-TY exhibit excellent biocompatibility, and can be employed as fluorescent imaging dyes for the visualization of microbial (both live and dead) and HeLa cells. Interestingly, we also clearly observed that CDs-TY had no adverse effect on the growth and reproduction of microbes, which provides strong evidence regarding the biosafety of CDs-TY.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...