Kinetics analysis of indocyanine green based on a novel mouse model to distinguish between tumor and inflammation
Abstract
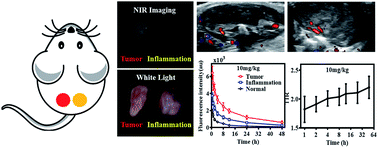
Near-infrared (NIR) imaging with indocyanine green (ICG) has been proven to be feasible for the visualization of tumor and enables real-time guidance during tumor resection. However, ICG is a non-receptor-specific NIR dye that also accumulates in other hyperpermeable tissues such as inflammatory tissues. In this study, we found visible differences between tumor and inflammation in 6 oral cancer patients by obtaining NIR images after 24 hours of 0.75 mg kg−1 ICG injection. In order to obtain the optimal ICG dose and observation time for better discrimination effect, we constructed the sponge implant model of angiogenesis and subcutaneous tumor model in the same C3H mice for further study. This mouse model was the first to prove the feasibility of ICG-NIR imaging and the difference between tumor and inflammation was successfully acquired in the model. Studies on this model avoid the interference of individual differences between tumor and inflammation and revealed the causal relationship between tissue permeability and fluorescence. The difference between the ICG kinetics of the tumor and inflammatory tissues was studied based on this mouse model. Results showed that the tumor-to-inflammation ratio (TIR) of fluorescence intensity was dose independent and increased with time, indicating that more ICG leakage and less clearance in tumors may lead to brighter NIR imaging than in inflammations. Thus, we recommend a high ICG injection dose and long observation time in order to better differentiate between tumor and inflammation by NIR imaging.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...