Extracellular recordings of bionic engineered cardiac tissue based on a porous scaffold and microelectrode arrays†
Abstract
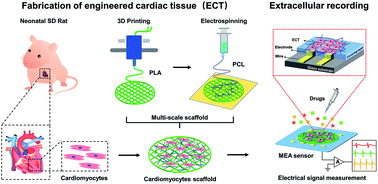
Cardiovascular disease remains the leading threat to human life and health, however, a powerful method to mimic the heart in vitro to study the mechanisms of drug therapy on cardiovascular disease is still lacking. In this work, bionic engineered cardiac tissue (ECT) based on a porous scaffold was fabricated, and microelectrode arrays (MEAs) were utilized for extracellular electrophysiological recording. Polylactic acid (PLA) and poly-ε-caprolactone (PCL) were used to fabricate the porous scaffold via 3D printing and electrospinning, and then cardiomyocytes from neonatal Sprague Dawley (SD) rats were cultured on the PLA/PCL scaffold to construct the ECT. The strength and biocompatibility of the scaffold were verified via evaluating the cell viability and mechanical beating status. A set of MEA sensors and a home-made detection system were designed, and the ECT was coupled with the MEA sensors for electrophysiological evaluation. The functionality of the ECT was verified via administrating isoprenaline (ISO). This work provides a new approach for evaluating ECT, which is expected to be applied to pharmaceutical studies.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...