A nano-sized chitosan particle based electrochemical aptasensor for sensitive detection of P. aeruginosa
Abstract
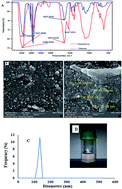
In this research, a glassy carbon electrode (GCE) was modified with nano-sized chitosan particles (NCs) by the drop-casting method for ultrasensitive detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa). NCs act as a novel platform for the aptamer-based sensor (aptasensor) for sensitive and simultaneous detection of P. aeruginosa. This system is based on a P. aeruginosa-binding aptamer, which is covalently connected to the surface of the GCE which has been in turn modified by the NC in order to form a sensitive layer and improve the performance of the aptasensor. In order to investigate the conductivity of the aptasensor and its electrochemical properties, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and cyclic voltammetry (CV) techniques were used. A low detection limit of 3 CFU mL−1, wide linearity of 101–107 CFU mL−1 for the detection of P. aeruginosa and high sensitivity for the aptasensor, which are obtained under optimized conditions, have been proposed. To detect P. aeruginosa in blood serum samples, the prepared aptasensor was successfully applied. This aptasensor also showed excellent stability with satisfactory electrochemical performance, reproducibility, and selectivity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...