Volatile component analysis in infant formula using SPME coupled with GC×GC-TOFMS†
Abstract
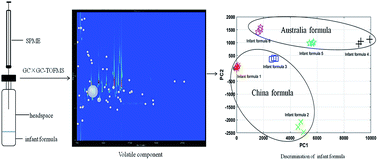
The presence of volatile components is an important quality criterion for infant formula, which can affect the aroma and appetite stimulation. In this study, a convenient and efficient method has been established to analyze the volatiles in infant formula samples and provide a comprehensive understanding of their sensory qualities using solid-phase micro-extraction (SPME) with comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography coupled to time-of-flight mass spectrometry (GC×GC-TOFMS). The modulation parameters were 5 s, 0.80 s, and 1.70 s. NIST retrieval was completed using TOFMS software with a matching degree > 700 and manual identification with retention indexes. A total of 173 volatiles were obtained. According to principal component analysis (PCA), aldehydes, ketones, and esters were selected as the principal components. Furthermore, we found that infant formula lacked terpenoids and was enriched in thermal-induced compounds in our study. The results showed that the established method can be used to effectively analyze and evaluate aroma components in infant formula.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...