An anti-influenza virus activity-calibrated chemical standardization approach for quality evaluation of indigo naturalis
Abstract
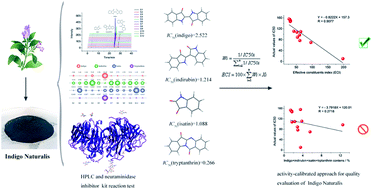
The quality evaluation of herbal medicine is the basis of its clinical application and industrial development. Multi-component determination is the main method of quantitative evaluation, but the results sometimes fail to accurately reflect the overall activity of herbs due to the significant activity variation of different components. In this manuscript, we tried to use an activity-calibrated chemical standardization approach to evaluate the activity of the antiviral herb indigo naturalis. Initially, the IC50 of indigo, indirubin, isatin and tryptanthrin inhibiting neurotyrosine kinase was determined and the results were 2.522, 1.214, 1.008 and 0.266 mg mL−1, respectively. Through reciprocal normalization transformation, the equation of effective constituents index (ECI) was established and ECI = 100 × (Xindigo × 0.068 + Xindirubin × 0.139 + Xisatin × 0.156 + Xtryptanthrin × 0.637). Then, the inhibitory effects of 12 batches of indigo naturalis on neurotyrosinase activity were measured. Meanwhile, the contents of four active ingredients in each sample were also determined using the HPLC method. Linear regression analysis results suggested that the correlation between the ECI and actual inhibition of neuraminidase activity was the highest and the correlation coefficient R was 0.9077. The ECI has a good association with clinical efficacy similar to a biological assay. We believe that this study method provides good operability, high precision and low cost and it will be of great utility in studies of other herbs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...