A highly efficient fluorescent probe based on tetrahydroxanthylium–coumarin for the detection of bisulfite in mitochondria†
Abstract
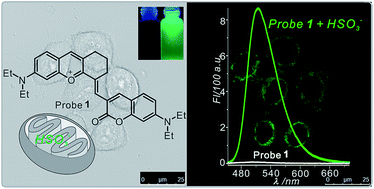
The addition of bisulfite to an electron-withdrawing double bond has been reported for the design of a bisulfite probe; however, the selectivity of this reaction is usually influenced by an oxidation reaction with hypochlorite. Herein, a probe (probe 1) with tetrahydroxanthylium and coumarin units was designed for the detection of bisulfite. The probe 1 exhibited high selectivity, an obvious colour change from blue to yellow and a large turn-on signal (144-fold enhancement) with green emission towards bisulfite in an acetonitrile-phosphate buffered saline (1 : 9, v/v) solution. In addition, an excellent linear relationship between the fluorescence intensity at 514 nm and bisulfite concentration (0–2 equivalent) was obtained. Moreover, the response time of the probe 1 towards bisulfite was within the order of several seconds, and the detection limit was calculated to be 22.8 nM. The mechanism of the detection reaction was proved by both the 1H NMR analysis and time-dependent density functional theory (TDDFT) calculations. The results of the fluorescence co-localization studies demonstrate that the probe 1 is a mitochondria-targeted fluorescent probe that can be used for the bioimaging of bisulfite in living HeLa cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...