Ribonuclease H-cleavable and recombinase-quenching fluorescent probes for the real-time detection of strand invasion based amplification†
Abstract
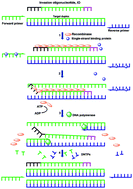
SIBA is an established nucleic acid amplification method that is used as an alternative to polymerase chain reaction (PCR). SIBA reactions are performed at low and constant temperature, obviating the need for the sophisticated instruments required for time-consuming thermal cycling. The products of SIBA reactions are typically visualized using intercalating dyes that are limited to detection of a single target per reaction tube. In this study, we developed two new alternative probe chemistries, RNase H-cleavable and recombinase-quenching probes, for real-time detection of SIBA reaction products. The performances of RNase H-cleavable and recombinase-quenching probes were compared with those of an intercalating dye (SYBR Green) and previously developed LNA probe chemistry. All detection chemistries exhibited relatively high analytical sensitivity and specificity and were compatible with a rapid method for processing of clinical specimens. The sensitivities of SYBR Green, LNA, RNase H-cleavable, and recombinase-quenching probes for detection of group A streptococcus (GAS) from clinical specimens were 100%, 96%, 100%, and 100%, respectively. LNA probe chemistry displayed the weakest performance in terms of sensitivity and detection time. All chemistries detected GAS from clinical specimens with 100% specificity and allowed for rapid detection of GAS from clinical specimens within 15 min (from sample processing to results). The newly developed detection chemistries displayed superior performance to the previous chemistries and could be used to facilitate rapid diagnosis of infectious diseases in point-of-care or central laboratory settings.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...