A label-free and enzyme-free aptasensor for visual Cd2+ detection based on split DNAzyme fragments†
Abstract
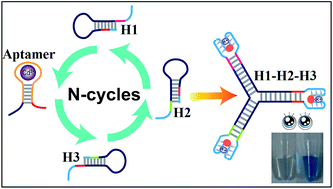
A label-free and enzyme-free three-way junction sensing system has been proposed for the amplified detection of Cd2+ based on split G-quadruplex DNAzyme fragments. Three hairpin structures were designed as the building blocks (hairpins 1, 2, and 3) to construct the three-way G-quadruplex junction. In the presence of Cd2+, the combination of Cd2+ and the aptamer initiated branch migration of hairpins to form an unstable complex. Then Cd2+–aptamer dissociated from the complex, acting as a catalyst to trigger the hybridization of additional branched junctions. Thus, the 3 : 1 split G-quadruplex fragments of those hairpins were brought into close-enough proximity to form a G-quadruplex. After addition of hemin, numerous intact G-quadruplex/hemin DNAzymes were generated, leading to an intensified color change observed by the naked eye. The biosensor exhibits excellent selectivity and high sensitivity for Cd2+ with a detection limit as low as 10 pM. The biosensor is simple and convenient in operation without labeling, washing, and modification, which makes it suitable for routine monitoring of Cd2+.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...