Micellar catalysis of an iron(iii)-MOF: enhanced biosensing characteristics†
Abstract
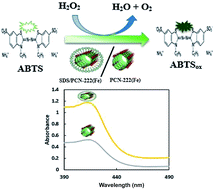
Recent years have seen an enormous growth of interest in enzyme mimics based on porous materials as a substitute for natural enzymes. This interest has been increased to a considerable extent due to the fact that they have outstanding chemical and structural features. Herein, Zr6O8(H2O)8(FeCl-tcpp)2(PCN-222(Fe)) was synthesized via a solvothermal approach with Zr6 clusters as nodes and Fe–TCPP (TCPP = tetrakis(4-carboxyphenyl)porphyrin) as a heme-like ligand and was characterized by various techniques such as XRD, TEM, SEM, XPS, UV-vis and IR. Also, since the achievement of high enzyme-like activity of some nanoparticles has attracted widespread interest in recent years, for the first time, we have applied a significant approach by modifying PCN-222(Fe) with sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) micelles (SDS/PCN-222(Fe)). In an attempt to explore the significance of this procedure, initially, peroxidase and catalase-like activity were investigated through a reaction with a chromogenic substrate 2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) diammonium salt (ABTS). Based on the high peroxidatic activity of SDS/PCN-222(Fe), a visual, sensitive and reliable method was established for detection of H2O2 with a linear range of 3–200 μM and limit of detection (LOD) of 2 μM. Also, as an implication of these findings, the SDS/Zr6O8(H2O)8(FeCl-tcpp)2 (SDS/PCN-222(Fe)) based system could also be used for glucose assay with a LOD of 3 μM indicating potential applications in clinical medicine. In order to prove this hypothesis, the glucose detection in human serum was determined. Finally, on the basis of SDS/PCN-222(Fe) performance, three natural antioxidants, gallic acid (GA), tannic acid (TA), and ascorbic acid (AA) were applied to explore antioxidant capabilities.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...