Study of chromatographic fractions from carbon dots isolated by column chromatography and a binary gradient elution via RP-HPLC†
Abstract
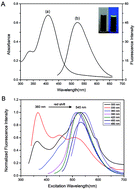
Carbon dots (C-dots) have abundant functional groups on their surface, which affect their luminescence properties, detection and structure. Therefore, it is necessary to purify the synthesized C-dots by certain preparative chromatography, e.g. silica gel column chromatography and reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC). RP-HPLC coupled with UV absorbance detection has been applied for studying the chromatographic behavior of C-dots which can be prepared by one-step calcination of the precursors citric acid and urea. Herein, we study in detail the effects of gradient elution conditions and the appropriate flow rate of the mobile phase on the RP-HPLC of C-dots. We investigated the performance of different proportions of precursors and found the best proportion of citric acid and urea for obtaining C-dots. By using silica gel column chromatography, we get the best fraction which did not have a bathochromic shift (510–540 nm) when excited by 340–460 nm, while other fractions have a bathochromic shift (420–530 nm) when excited by 340–460 nm. Our results indicate that C-dot fractions with a better fluorescence performance and size distribution can be obtained via purification. The C-dot fractions emitted stable orange and yellow luminescence colors under a single-wavelength UV light. It is anticipated that our silica gel column chromatography and RP-HPLC methodology will open a new avenue to obtain excitation-independent C-dots.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...