Chiral analysis of β-methylamino alanine (BMAA) enantiomers after (+)-1-(9-fluorenyl)-ethyl chloroformate (FLEC) derivatization and LC-MS/MS†
Abstract
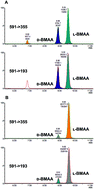
β-Methylamino-L-alanine, a neurotoxin first isolated from the seeds of cycad tree Cycas circinalis, is widely spread in a variety of environments. New sensitive techniques and robust methodologies are needed to detect its presence in complex biological samples and to further understand its biochemical properties. In this context, the determination of the enantiomeric composition of natural BMAA is of great importance. In this study, a simple and easily implemented LC-ESI-MS/MS method was developed to determine the presence of both D- and L-BMAA enantiomers in samples of cycad seed (Cycas micronesica). The samples were subjected to enzymatic hydrolysis to avoid racemization that occurs during strong acid hydrolysis. Derivatization with (+)-1-(9-fluorenyl)-ethyl chloroformate (FLEC) was performed prior to LC-ESI-MS/MS to produce chromatographically separable derivatives of D- and L-BMAA. Together with the retention time, two MRM transitions and their peak area ratios were used to identify the compounds. The LOQ obtained was 0.3 μg BMAA per g wet weight for each enantiomer. Method repeatability was within 3 RSD% both intraday and interday and accuracy was 98–108%. An accurate enantiomeric composition was obtained from the samples of cycad seed, where L- and D-BMAA were detected at 50.13 ± 0.05 and 4.08 ± 0.04 μg BMAA per g wet weight respectively (n = 3).
- This article is part of the themed collections: Analytical Methods Recent HOT articles and Analytical Methods Recent Open Access Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...