Synthesis of novel fluorescent copper nanomaterials and their application in detection of iodide ions and catalysis†
Abstract
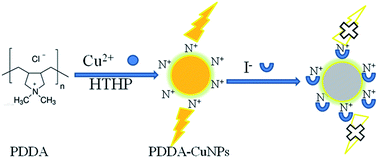
In this work, polydimethyldiallylammonium chloride (PDDA) was used as a template and protective agent to synthesize high-fluorescence copper nanoparticles (CuNPs) at high temperature and high pressure. The high-fluorescence CuNPs were characterized by fluorescence spectroscopy (FL), ultraviolet-visible absorption spectroscopy (UV-vis), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), energy spectrum analysis (EDS), Fourier infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The fluorescence of CuNPs can be effectively quenched based on iodide, so high-fluorescence CuNPs were used as a fluorescent probe to detect iodine ions. The degree of fluorescence quenching of CuNPs showed a linear relationship (R = 0.9820) when the iodine concentration was 1–100 μmol L−1, and the minimum detection limit was 0.45 μmol L−1 (S/N = 3). The iodine ion was selected by high-fluorescence CuNPs, and the iodine ions in the actual water samples were detected. Based on this, the ultra-sensitive and unmarked detection of iodide was completed. In addition, we found that the copper nanomaterials also have catalytic ability to accelerate the reduction of methylene blue dye by phenylhydrazine.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...