An electroanalytical platform for nereistoxin-related insecticide detection based on DNA conformational switching and exonuclease III assisted target recycling†
Abstract
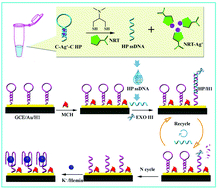
In this work, an electroanalytical platform for nereistoxin (NRT)-related insecticide detection is proposed on the basis of NRT induced DNA conformational switching and exonuclease III (Exo III) assisted target recycling. NRT-related insecticides were first hydrolyzed and converted into NRT with two thiol groups (–SH). Then, a cytosine–Ag+–cytosine (C–Ag+–C) mismatched base pair was adopted to induce a blunt-ended hairpin configuration of HP DNA. In the presence of converted NRT, it could take up Ag+ from HP DNA to change its conformation from a hairpin to single-stranded structure (HP ssDNA). Thereafter, the obtained HP ssDNA was further hybridized with an H1 hairpin probe on the electrode surface to trigger the Exo III cleavage process, releasing HP ssDNA for recycling leaving the G-quadruplex fragment of H1, which was used for hemin/G-quadruplex complex formation. The reversible redox reaction of Fe(III)/Fe(II) of hemin gave a remarkable electrochemical response for quantitative determination of the NRT-related insecticides. As an analytical model, a low detection limit of 3.9 ng L−1 and a wide linear range of 0.01–1500 μg L−1 with excellent selectivity were achieved for cartap detection. The proposed method also displayed great applicability for cartap detection in agricultural products.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...