Ultrasensitive electrochemical DNA biosensor based on a tetrahedral structure and proximity-dependent surface hybridization†
Abstract
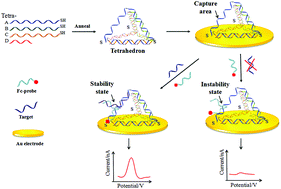
The DNA tetrahedron has developed a broad spectrum of applications in biosensor construction thanks to its excellent mechanical rigidity and structural stability. However, how to construct a highly sensitive biosensor using a DNA tetrahedron is still a challenge. In this work, an ultrasensitive electrochemical biosensor based on a DNA tetrahedral nanostructure was developed with the help of synergy from proximity-dependent hybridization. To decrease the steric hindrance of DNA tetrahedra to proximity-dependent hybridization, the detection signal was set on the inclined side chain structure of a DNA tetrahedral sensing system. Additionally, when the target hybridized with the DNA probe, the ferrocene (Fc) labeled on the end of the DNA probe was driven close to the surface of the biosensor, providing a sensitive faradaic current. The experimental results exhibited a good linear relationship from 1 fM to 10 pM with a linear correlation coefficient of 0.9977, and a high sensitivity with a detection limit of 0.2 fM. Our DNA biosensor also showed good stability according to electrode characterization and target detection at different time scales and the anti-jamming capabilities in a complicated biological extraction environment were excellent. The electrochemical sensing system established here has greatly improved the detection sensitivity of a DNA biosensor based on a DNA tetrahedron, which will further promote its practical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...