Non-invasive detection of glucose via a solution-gated graphene transistor†
Abstract
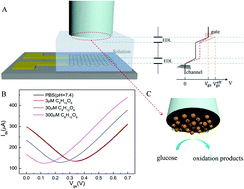
Owing to its high sensitivity, a solution-gated graphene transistor has rapidly emerged as a cutting edge technology in electrochemical sensing. In this work, composites of gold nanoparticles and reduced graphene oxide were synthesized on a glassy carbon electrode by using the electrodeposition method. A modified glassy carbon electrode was used as the gate electrode and assembled into the solution-gated graphene transistor device along with the graphene channel for a non-invasive glucose detection. The sensing mechanism was based on the change in current in the channel of the device caused by the addition of glucose, of which electro-oxidation on the surface of the gold nanoparticles and reduced graphene oxide led to a change in equivalent gate voltage, and consequently, affected the channel carrier concentration. The self-amplification effect of transistors was utilized in our sensors, which resulted in a detection limit that was 10 times lower than those of conventional electrochemical sensors. Compared to traditional enzymatic transistor sensors, the novel solution-gated graphene transistor nonenzymatic sensors based on gold nanoparticles and reduced graphene oxide demonstrated significant sensing advantages, such as a simple structure, wide linear range from 10 μM to 400 μM and 400 μM to 31 mM, and low detection limit down to 4 μM. The chemicals coexisting in human sweat e.g. sodium chloride, urea, and lactic acid imposed no distinct interference for the glucose detection. Therefore, we achieved a non-invasive detection of glucose in the artificial sweat samples with satisfactory sensing results. This work demonstrates an effective route for non-invasive glucose testing in practical clinical diagnosis by using nonenzymatic, solution-gated graphene transistor devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...