Real-time monitoring of electroreduction and labelling of disulfide-bonded peptides and proteins by mass spectrometry†
Abstract
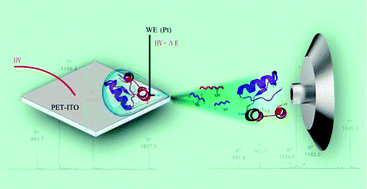
The accurate determination of disulfide bonds for protein identification is in high demand. In this study, a simple electrochemical-mass spectrometry (EC-MS) method that possesses advantages of real-time information, simultaneous disulfide bond electroreduction and tagging was developed. In this EC-MS, an ITO glass corner functions as a counter electrode and spray system, and allows the direct sampling of the droplet-scale reacting solution in real-time. The application of this method was successfully demonstrated by electrochemical reduction of oxidized glutathione (GSSG) with one disulfide bond as well as insulin with multiple disulfide bonds. The preferred electroreduction of intermolecular-bonded disulfides for insulin has been observed and the intramolecular bond was not favored. Moreover, simultaneously tagging the formed thiol residues from electroreduction of GSSG using electrogenerated intermediates such as dopamine orthoquinone (DQ) and benzoquinone (Q) was performed. A proof-of-concept was also demonstrated with a large molecule, β-lactoglobulin A. The relationship between signal strength and operating parameters was also studied. This method successfully detected the reduction reaction of the disulfide bond in the polypeptide and protein. The detection limit (S/N ≥ 3) is 0.398 μg mL−1. These results suggest that this EC-MS platform can count cysteine moieties in proteins using a single drop of sample and in real-time and is promising for protein identification experiments.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...