Carbon dot-based inverse opal hydrogels with photoluminescence: dual-mode sensing of solvents and metal ions†
Abstract
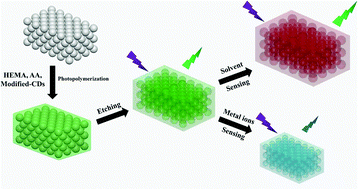
A dual-mode sensing platform, involving fluorescence and reflectance modes, has been demonstrated for highly sensitive and selective detection of solvents and metal ions based on carbon dot-based inverse opal hydrogels (CD-IOHs). In this work, CD-IOHs have been first synthesized via the typical templating technique. Two kinds of CDs, including solvent and Cu(II) ion sensitive CDs, have been incorporated into the matrix of IOHs during the co-polymerization of acrylic acid (AA) and 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA). The CD-IOHs not only appear green under daylight but also exhibit stable photoluminescence (PL) under UV light owing to the stop-band effect of photonic crystals and the quantum effect of CDs, respectively. By using these two optical phenomena, for solvent sensing, the CD-IOHs change their colors from green, yellow, and red to a semitransparent state and show good linear sensing with the ethanol content varying from 0 to 45% in reflectance mode, while their PL intensities exhibit a nonlinear detection trend: first an increase and then a decrease with the ethanol content in fluorescence mode. Remarkably, as for metal ion sensing, the CD-IOHs have high selectivity for Cu(II) ions via the specific PL quenching effect of Cu(II) ion sensitive CDs. Furthermore, the CD-IOHs show good linear detection in both modes and a wide linear detection range from 0.1 μM to 7 mM. Thus, high selectivity, colorimetric detection, a broad linear detection range, and dual-mode sensing can be realized using the CD-IOHs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...