Tracing the molecular dynamics of living mitochondria under phototherapy via surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy†
Abstract
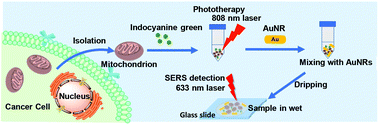
Subcellular mitochondrion has become a target for improving the therapeutic efficiency and reducing side damage to normal cells via a combination of many therapeutic strategies. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms associated with cell death induced by subcellular dysfunction remain unknown or disputed. In this study, we investigated the dynamic molecular changes of living mitochondria upon phototherapy (photothermal therapy plus photodynamic therapy, PTT & PDT) by surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy (SERS) and intended to disclose the photo-induced cell death route in breast cancer cells (MCF-7) taking into account the mitochondrion. Indocyanine green (ICG), a Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved clinic blood-injection near-infrared angiographic contrast agent and a PTT & PDT drug, was used for the evaluation of the phototherapy effect. The results revealed that the content of phenylalanine (Phe) in mitochondria evidently increased during the phototherapy-induced cell death process. Moreover, the phototherapy-induced cell apoptosis was mainly regulated through the DNA structures. We expect that the understanding of mitochondrial molecular stress responses will be helpful for the diagnosis and therapy of cellular processes associated with mitochondria and provide valuable guidance for the further design and development of more effective therapeutic platforms and methods at the sub-cellular level.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...