A microscale solid-phase microextraction probe for the in situ analysis of perfluoroalkyl substances and lipids in biological tissues using mass spectrometry†
Abstract
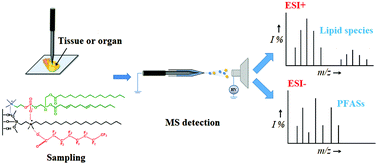
The simultaneous analysis of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) and lipids in biological tissues is of importance, especially for in situ and microscale analysis, because it provides significant information to understand the relevance of content, composition, and distribution of lipids to the bioaccumulation of PFASs as well as lipid metabolism affected by the biotoxicity of PFASs. In this study, we report the development of a novel ambient mass spectrometry method for the rapid, in situ, and microscale analysis of PFASs and lipids simultaneously in biological tissues for the investigation of their biological correlation. A microscale solid-phase microextraction (SPME) probe with a probe-end diameter of several-μm was employed for in situ and microscale sampling of biological tissues after PFAS exposure. The SPME probe showed a desirable capacity for the enrichment of PFASs and lipid species simultaneously. After sampling and extraction, the loaded SPME probe was directly applied for nanoESI-MS analysis under ambient and open-air conditions. A high-resolution Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance (FTICR) mass spectrometer operated in the field-induced mode was introduced to record mass spectra using fast polarity switching between positive and negative ion detection. Most of the lipid species were recorded in the positive ion mass spectrum, and PFASs were recorded in the negative ion mass spectrum. By using the developed method, the in situ analysis of PFASs and lipids in the muscle, brain, heart, kidney, liver, and intestine of zebrafish was realized. In addition, simultaneously imaging PFASs and lipids in individual Daphnia magna was successfully achieved for the investigation of their biological correlation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...