A biomimetic fluorescent nanosensor based on imprinted polymers modified with carbon dots for sensitive detection of alpha-fetoprotein in clinical samples
Abstract
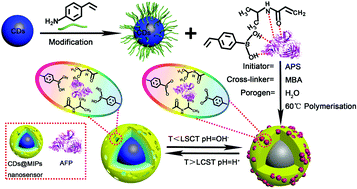
A biomimetic fluorescent nanosensor based on molecularly imprinted polymers modified with carbon dots (CDs@MIPs) has been prepared for rapid, selective and sensitive detection of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in clinical samples. The nanosensor was produced using vinyl-functionalized CDs (V-CDs) as transducer elements and support materials, AFP as the template protein, N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAM) and 4-vinylphenylbronic acid (VPBA) as the thermo-responsive and pH-responsive monomer, respectively, and ammonium peroxodisulphate (APS) and N,N′-methylene bisacrylamide (MBA) as the initiator and cross-linker, respectively. The newly synthesized nanosensor was characterized by FT-IR, TEM, XRD and elemental analysis, which unambiguously confirmed the successful formation of the nanosensor. The fluorescence quenching degree of CDs@MIPs exhibited a good linear response to AFP in a concentration range of 10 to 100 ng mL−1, the limit of detection (LOD) of 0.474 ng mL−1, and high recoveries at three spiking levels of AFP ranging from 97.05% to 102.00%, with relative standard deviations (RSDs) below 4.2% being obtained. Moreover, the proposed CDs@MIPs were successfully exploited to detect AFP in human serum samples. This study successfully established a novel method for rapid, convenient, and highly sensitive and selective detection of AFP, which provides new ideas for the detection of tumor markers.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...